
Seaweed fiber ultrasonic vibrating screen is a screening equipment designed for fine fiber materials. It combines ultrasonic high-frequency vibration and mechanical vibration technology to effectively solve the problems of entanglement, agglomeration, and electrostatic adsorption of seaweed fiber during the screening process. The screening accuracy can reach 80-500 mesh (180μm-25μm), which is suitable for high-precision screening requirements. Its core advantage lies in high-precision screening and anti-blocking net capabilities, which is suitable for particle size classification, impurity removal and homogenization of seaweed fiber.
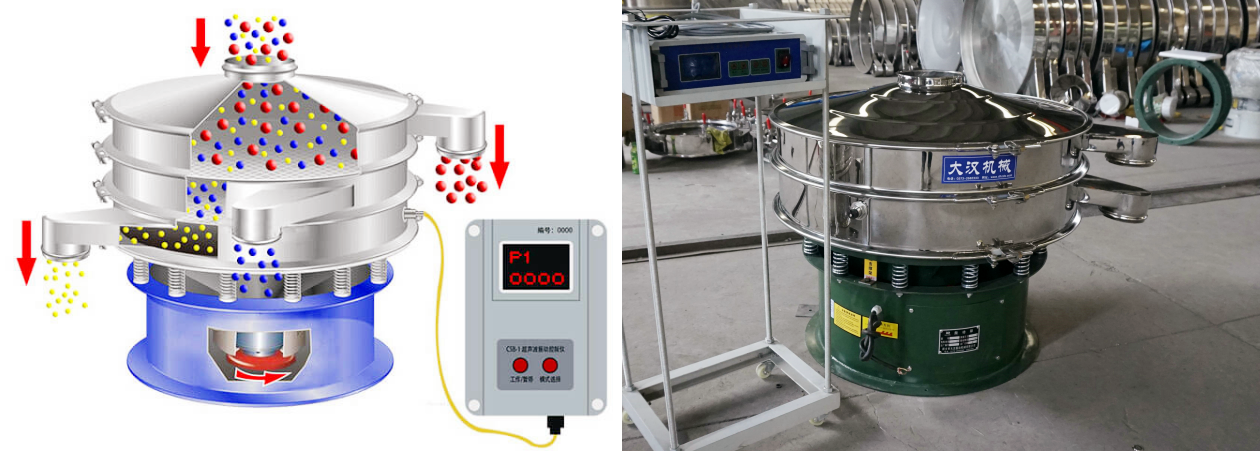

Seaweed fiber is in the form of light filaments. It has a small specific gravity and is tough. Ordinary screens are prone to floating and blocking the net. Ultrasonic waves can effectively break up the fibers and increase the net penetration rate
The particle size range of seaweed fiber is fine powder to micro powder, which is suitable for screening 25~500μm seaweed powder, fiber end particles, etc. Ultrasonic vibration improves the fine mesh screening accuracy
The humidity state of seaweed fiber is slightly moist to dry powder, which is suitable for dry or slightly moist seaweed powder/fiber
The seaweed fiber ultrasonic vibrating screen is based on the traditional vibrating screen and superimposed with ultrasonic technology. Its working principle may be:
①The vibration motor drives the screen to produce three-dimensional vibration, so that the seaweed fiber is initially dispersed and moved on the screen surface.
②The ultrasonic transducer converts high-frequency electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical waves. On the basis of mechanical vibration, the screen is superimposed with high-frequency, small-amplitude ultrasonic vibration.
③Compound vibration can effectively destroy the agglomeration and entanglement between seaweed fibers, reduce the surface tension between fibers, and make it easier for them to pass through the screen, thereby achieving efficient and rapid screening and grading of seaweed fibers.
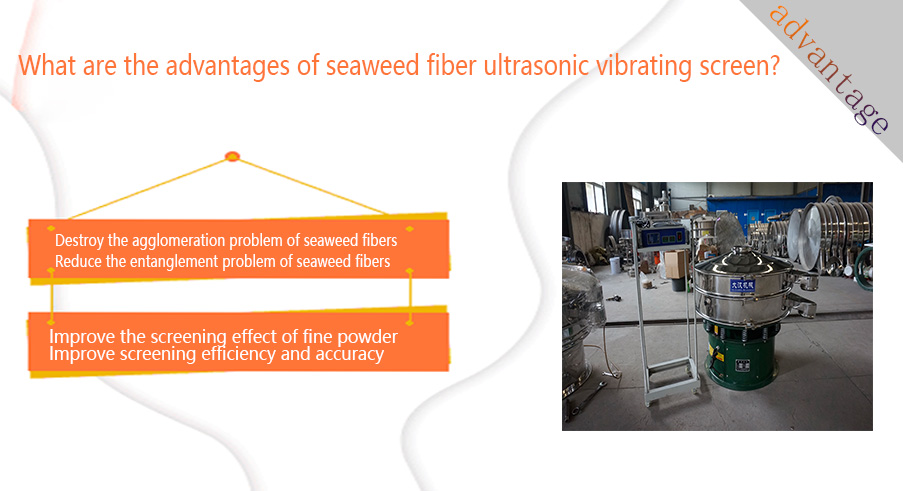
Destroy the agglomeration problem of seaweed fibers: high-frequency and small-amplitude ultrasonic vibration acts on the screen, generating high acceleration, which can instantly destroy the intermolecular forces between seaweed fibers, effectively disperse the agglomerated fibers, and make them contact the screen in the form of smaller units.
Reduce the entanglement problem of seaweed fibers: The addition of ultrasound generates high-frequency vibration waves on the surface of the screen, which helps to straighten out the entangled fibers and reduce the mutual hooking between the fibers. High-frequency vibration can change the movement trajectory of the fibers on the surface of the screen, reduce their residence time at the edge of the mesh, and reduce the probability of entanglement.
Improve the screening effect of fine powder: Ultrasonic vibration can make the fine seaweed fiber particles suspend near the surface of the screen, reduce their contact with the screen, overcome surface force and air resistance, and more easily pass through the mesh. High-frequency vibration can also destroy the viscosity between the fine powder layers, increase their screening rate, and reduce the generation of dust.
Improve screening efficiency and accuracy: By solving problems such as agglomeration, entanglement and blockage, the ultrasonic vibrating screen can maintain the effective screening area of the screen and increase the passing speed of the material. More uniform material dispersion and less clogging also means higher screening accuracy, which can more accurately separate the seaweed fibers of the desired particle size.

The recommended mesh size for seaweed fiber screening mainly depends on the specific application scenario (such as for food, cosmetics, medicines, feed or degradable materials), because different downstream products have different requirements for fiber thickness, purity and touch.
|
Application field |
Sieve mesh range |
Particle size range (μm) |
Description |
|
Food additives |
80~200 mesh |
180μm~75μm |
Can ensure the fineness of the fiber and good palatability, commonly used in functional foods and beverage ingredients |
|
Medical raw materials |
120~300 mesh |
125μm~48μm |
Requires higher purity and fineness, convenient for capsule tableting or granule mixing |
|
Cosmetics (skin care products) |
200~400 mesh |
75μm~38μm |
The particle size needs to be fine to prevent skin irritation, used in facial masks, scrubs, cleansers, etc. |
|
Aquatic/livestock feed |
60~120 mesh |
250μ m~125μm |
Sieve out coarser fiber components, retain nutrition, and improve palatability |
|
Biodegradable materials |
40~100 mesh |
400μm~150μm |
High requirements for particle size consistency to ensure uniform distribution of reinforcing fillers |
|
Alginate byproduct separation |
20~80 mesh |
850μm~180μm |
Used to separate incompletely dissolved seaweed residues and crude fibers from the extract |
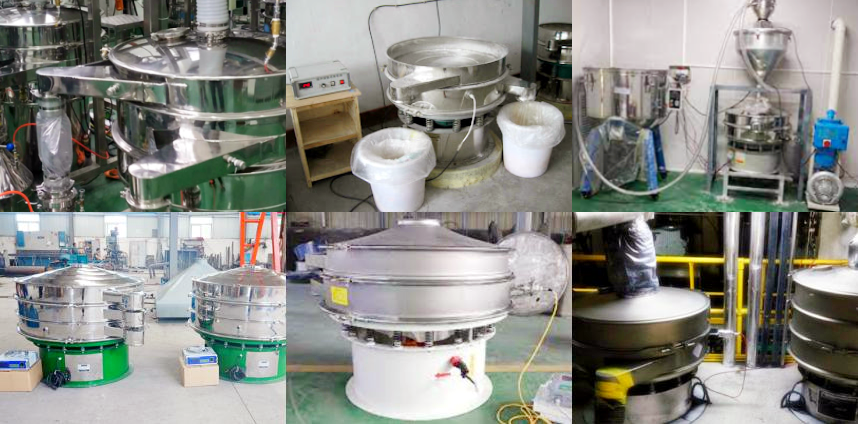

Fine classification of seaweed fiber to obtain products of different particle sizes: Many food additives, such as sodium alginate, carrageenan, etc., have strict requirements on the particle size of seaweed fiber. For example, the production of a thickener with a specific viscosity may require sodium alginate powder with a specific particle size range. The ultrasonic vibrating screen can accurately classify the ground seaweed fiber powder into different particle size ranges (for example, 80 mesh, 120 mesh, 200 mesh or above).
Removal of impurities in the production process of seaweed fiber: After the initial processing of seaweed, coarse impurities such as sand, shell fragments, and incompletely crushed seaweed tissue may be mixed. Although ordinary vibrating screens may be used for primary screening, for finer impurity removal, especially when the seaweed fiber has a certain viscosity, ultrasonic vibrating screens can more effectively separate these impurities from the fiber and improve the purity of the seaweed fiber.
Wet seaweed fiber processing and preliminary dehydration: In some seaweed fiber extraction or modification processes, the fiber may exist in the form of wet slurry. The ultrasonic vibration of the seaweed fiber ultrasonic vibrating screen can reduce the viscosity of the slurry and increase its fluidity on the screen, thereby more effectively separating the liquid and achieving preliminary solid-liquid separation or dehydration.
Processing of seaweed fiber with special forms: For some special applications, seaweed fiber may need to be cut into short fibers of a specific length. Ultrasonic vibrating screens can be used to screen out short fibers of uniform length and remove fibers that are too long or too short to improve the uniformity of the product. Ultrasonic waves help prevent the entanglement and agglomeration of short fibers during screening.

The mesh selection of seaweed fiber ultrasonic vibrating screen should be combined with the specific application scenario. Low mesh number can achieve efficient impurity removal, and high mesh number can ensure accurate classification. Dahan Machinery provides a full range of screen customization services from 5 mesh to 400 mesh, combining ultrasonic vibration and intelligent control technology to ensure the improvement of screening efficiency and product quality.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.